Lesson 7: LCA EDIP method, and QFD and EQFD methods
In this lesson, we’ll delve into two valuable methods, the EDIP (Environmental Design of Industrial Products) method and QFD (Quality Function Deployment) and its eco-centric counterpart EQFD (Environmental Quality Function Deployment). These methods are essential for assessing and integrating environmental considerations and consumer requirements into product design and development.
- EDIP METHOD
Overview of the EDIP Method:
- Environmental Design of Industrial Products (EDIP) was developed in Denmark from 1991-1996.
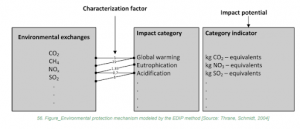
- It follows the “Mid-Point Approach” and focuses on various environmental categories with the ecological exchange as its starting point.
- EDIP evaluates impact categories like global warming, ozone depletion, acidification, eutrophication, photochemical oxidant creation, and abiotic resource depletion.
Impact Assessment and Normalization:
- EDIP introduces four waste categories: non-hazardous waste, hazardous waste, slag and ashes (inert waste), and nuclear waste.
- To compare contributions to different impact categories, normalization is performed.
- The reference year is 1990, and the basic scales are per capita of the considered area in relation to the world or Denmark.
- Normalization uses the environmental load (EL) from the average person in 1990 as a reference.
- Final weighting is done using a “Distance-to-Target” approach, aiming to meet Danish environmental objectives and international conventions.
- Recent improvements incorporate “platforms” of loads for European countries, normalization references for European countries, a European average, and even a “European Personal Equivalent” unit.
- The method is also adapted to China, leading to the “Chinese Equivalent.”
Cooperation and Consistency:
- EDIP aligns with international consensus on impact characterization.
- Collaboration between industry, universities, and authorities during its development ensures practical use and scientific rigor.
- Unlike indicator-based methods, EDIP’s weighting is less subjective, relying on scientific assessments.
- QFD AND EQFD METHODS
Introduction to QFD and EQFD Methods:
- QFD (Quality Function Deployment) and EQFD (Environmental Quality Function Deployment) methods address consumer requirements and stakeholder needs in product development.
- They help translate these requirements into technical design parameters and prioritize them.
- These methods use an asymmetric scale of 0-1-3-9 for evaluation, making it easier to assess crucial requirements.
Quality Function Deployment – QFD:
- QFD was developed by Yoji Akao in Japan in 1966 and gained prominence in 1972 through Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
- It was introduced in Europe in 1987.
- QFD focuses on integrating consumer requirements and needs into the product development process.
Environmental Quality Function Deployment – EQFD:
- EQFD identifies essential environmental parameters among various consumer requirements and stakeholder needs.
- It helps ensure that environmental considerations are incorporated into product development.
Conclusion:
- The EDIP method provides a comprehensive approach to assessing environmental impacts and is adaptable to various regions.
- QFD and EQFD methods facilitate the integration of consumer requirements and environmental considerations into product design and development.
- These methods use clear evaluation scales to prioritize important requirements, enhancing the quality and sustainability of products.