Lesson 1: Reasons for introducing ecodesign
Welcome to this lesson where we’ll delve into the importance of Ecodesign and its pivotal role in our future.
INTRODUCTION
- Ecodesign is a forward-thinking approach that integrates environmental considerations into product design and development.
- Its significance is underlined by increasing global environmental challenges and a pressing need for sustainable resource management.
- Ecodesign encompasses the entire product life cycle, promoting comprehensive environmental responsibility.
WHAT IS ECODESIGN?
- Ecodesign focuses on creating products that minimize environmental impact.
- It considers every stage of a product’s life cycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
- The goal is to prevent shifting environmental impacts from one stage to another.
WHY ECODESIGN?
- A disproportionate 20% of the world’s population utilizes a staggering 80% of global resources.
- Natural resources like energy and raw materials are finite.
- Ecodesign aims to decrease resource consumption during product creation, ensuring sustainable consumption patterns.
- With an escalating global population, energy demands are on the rise, underscoring the need for Ecodesign.
EU ENERGY CONSUMPTION
- The average EU household consumes approximately 6,000 kWh of electricity annually.
- By 2030, the EU’s fossil fuel demand is projected to skyrocket, with increasing reliance on imports.
- Alarmingly, only 5% of the EU’s oil requirements will come from local sources.
- The continued dominance of fossil fuels means rising CO2 emissions, with renewable energy playing a limited role.
UNDERSTANDING ENERGY TERMINOLOGY
- Primary Energy: The raw energy found in natural resources, unaltered by human processes. Examples include coal and sunlight.
- Final Energy: The energy ready for end-user consumption, like electricity from an outlet.
- Total Energy: Primary energy combined with the energy used in electricity generation, distributed across various sectors.
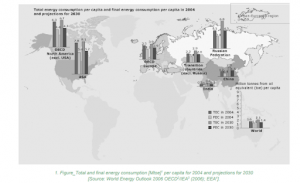
THE GLOBAL PICTURE
- OECD Europe comprises countries like Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, and the UK, among others.
- OECD America includes Canada, Mexico, and the USA.
- Eurasia and Middle East consist of countries spanning from Armenia to Yemen.
THE IMPERATIVE OF ALTERNATIVE ENERGY
- Fossil fuel combustion discharges harmful gases causing global warming, leading to:
- Climate shifts.
- Altered ecosystems.
- Melting glaciers.
- Rising sea levels.
- Habitat and biodiversity loss.
- The urgency of these consequences necessitates alternative energy exploration.
- Emphasis should be placed on renewables such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower.
CONCLUSION
- Ecodesign is not just a design philosophy, but an environmental imperative.
- Balancing consumption with sustainability is crucial in a resource-limited world.
- Adopting alternative energy sources and understanding their potential can pave the way for a brighter, greener future.
Thank you for joining us in understanding the importance of Ecodesign. Implementing its principles can make a significant difference in our world!