Lesson 6: The automotive value chain in 2025: four plausible scenarios
In this lesson, we will explore the potential future scenarios for the automotive value chain in the year 2025, driven by various factors and uncertainties.
Introduction
- The automotive value chain in 2025 will be shaped by a multitude of influential factors and drivers.
- The uncertainty surrounding these developments makes scenario-based thinking crucial for informed decision-making.
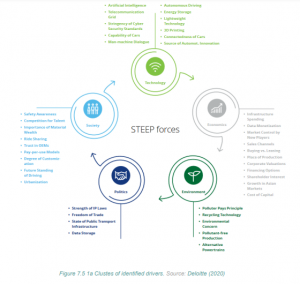
Key Drivers Shaping the Automotive Future
- The future of the automotive industry is influenced by drivers categorized into five areas:
- Social change
- Technology advancement
- Economic shifts
- Environmental trends
- Political developments
- These drivers have varying degrees of uncertainty and impact on Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) activities.
Example: 3D Printing
- 3D printing is a high-impact but uncertain driver with potential effects on the supply chain, manufacturing, and logistics.
- It offers advantages such as reduced prototype development time and in-house production but faces challenges like high production costs.
- Some drivers, like “customers’ and regulators’ safety awareness,” are more certain with significant impacts.
Identifying Critical Uncertainties
- Critical uncertainties are drivers with high uncertainty and significant impact.
- Examples include “alternative powertrains” and the “connectedness of cars.”
- These uncertainties are crucial for shaping distinct and meaningful scenarios.
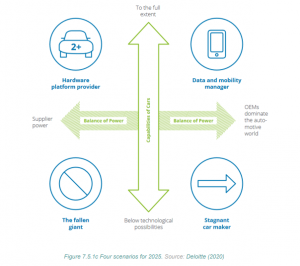
Scenario 1: “Data and Mobility Manager”
- In this scenario, connectivity is a differentiator.
- OEMs set industry standards and dominate the automotive sector.
- Innovative outsiders must adhere to OEM rules, and premium brands hold sway.
- OEMs provide an attractive talent pool.
Scenario 2: “Stagnant Car Maker”
- In this scenario, OEM lobbying prevents new high-tech players from entering.
- However, this strategy hinders technical development and innovation rollout.
- Safety concerns lead to a loss of consumer trust.
Scenario 3: “The Fallen Giant”
- This scenario envisions the car as a mere means of transportation.
- Technology hype wanes, reducing profit margins.
- Industry outsiders like Uber enter the market, focusing on affordable mass mobility.
- Private car ownership declines, and fleet management becomes vital.
Scenario 4: “Hardware Platform Provider”
- IT players disrupt the automotive value chain.
- OEMs mainly supply white-label cars to internet giants.
- OEMs thrive by offering superior infotainment and mobility platforms or maintaining a strong brand image.
- Revenue potential per vehicle decreases.
Implications for OEMs
- OEMs’ core businesses will undergo significant changes by 2025.
- New mobility concepts and competition threaten market shares and profits.
- Four potential futures for OEMs include becoming technology leaders, achieving stability through collaboration, survival through efficiency improvements, and setting up strategic partnerships with IT giants.
- Strategic decisions will be crucial for OEMs to navigate the evolving automotive landscape.
Conclusion
- The future of the automotive value chain in 2025 is uncertain, driven by various factors.
- Scenario planning helps decision-makers anticipate and adapt to potential developments.
- OEMs face significant challenges and opportunities in shaping the automotive industry’s future.
In this lesson, you’ve explored four plausible scenarios for the automotive value chain in 2025, driven by a range of factors and uncertainties. Understanding these scenarios is essential for industry stakeholders to make informed decisions and adapt to the evolving automotive landscape.