Lesson 5: PERCEPTION
In this lesson, we will delve into the crucial aspect of perception in autonomous vehicles, where the vehicle’s sensors and software work together to understand and interact with the surrounding environment.
- Introduction to Perception
- The human brain is exceptional at perceiving its surroundings, making quick judgments about the environment to ensure safety.
- However, replicating this capability in autonomous vehicles is a complex task.
- Autonomous vehicles rely on a combination of sensors to collect data, and perception and navigation software to interpret this data.
- Perception is essential for understanding “where am I?” and “what’s around me?”
- Reliable perception is vital for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
- Localization
- Localization determines the vehicle’s position and orientation relative to a map.
- There are two main approaches to localization: local (relative) and global (absolute).
- Local localization compares the current position to the previous one and is resource-efficient.
- Global localization uses external references like satellites (GNSS) or known landmarks.
- Combining both approaches is common for robust localization.
- GNSS offers global positioning but may not work well in obstructed environments.
- Mapping
- High-definition maps are crucial for autonomous vehicles.
- These maps are often not publicly available and need to be generated.
- The choice of map type depends on sensor types, computer capacity, localization algorithms, and more.
- Object Recognition
- Object recognition is fundamental for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles.
- It involves detecting and understanding objects in the vehicle’s environment.
- Humans perform object recognition effortlessly, but it’s challenging for computers.
- Deep learning is a promising technology for improving object recognition.
- Object recognition includes localization, classification, and semantic segmentation.
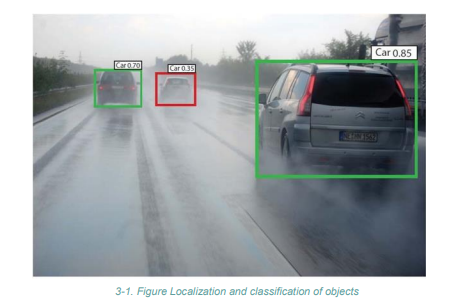

- Object Recognition Steps
- Pre-processing: Normalizes and adjusts the raw image.
- Feature extraction: Removes irrelevant information and extracts relevant features for classification.
- Classification: Connects the features map to predefined reference feature maps for each object class.
Conclusion
- Perception is a critical component of autonomous vehicles, enabling them to understand and interact with their environment.
- Localization, mapping, and object recognition are essential aspects of perception.
- Ongoing advancements in sensors, software, and deep learning are improving the ability of autonomous vehicles to perceive and navigate their surroundings.
- This foundational understanding of perception is vital for students and researchers working in the field of autonomous vehicles.