Lesson 2: AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES AND REGULATIONS
In this lesson, we will explore the complex landscape of regulations surrounding autonomous vehicles and how different regions of the world are approaching this transformative technology.
Introduction
- As autonomous vehicles become a reality on our roads, a myriad of questions arise about regulations and responsibilities.
- Who pays penalties for traffic violations by autonomous vehicles?
- How do authorities handle accidents involving autonomous vehicles?
- Are the current road regulations ready for the advent of autonomous vehicles?
- In this lesson, we will navigate the evolving regulatory landscape for autonomous vehicles.
- Europe
- The Vienna Convention on Road Traffic, established in 1968, initially required every vehicle to have a human driver in control.
- Amendments in 2016 allowed autonomous driving, but with the stipulation that the driver can override or deactivate the autonomous system.
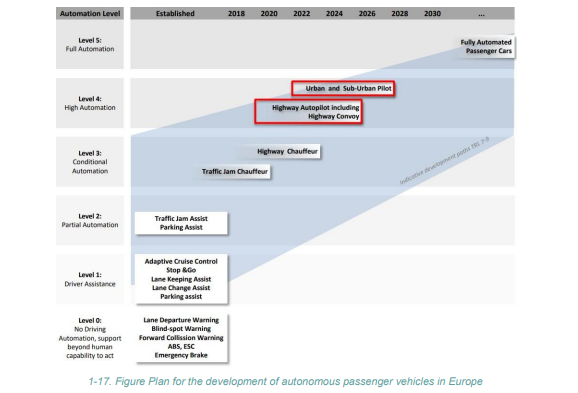
- Europe is actively researching and developing autonomous passenger vehicles, as seen in the European Road Transport Research Advisory Council’s (ERTRAC) development plan.
- Several European countries, including the UK, the Netherlands, France, Switzerland, Germany, Sweden, Spain, Austria, Finland, Greece, and Hungary, have introduced regulations or initiated projects related to autonomous vehicles.
- USA
- The United States, particularly states like Nevada, has been at the forefront of allowing autonomous vehicle testing on public roads.
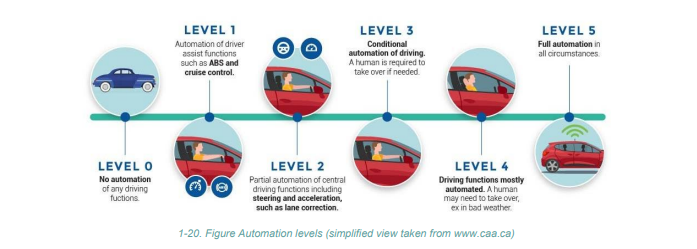
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) introduced a classification system for autonomous vehicles based on levels of autonomy, from Level 0 to Level 4.
- Each state has its own regulations for autonomous vehicles, emphasizing vehicle type approval, insurance, and driver attendance.
- States like Florida permit autonomous vehicles to operate without human drivers present.
- In 2017, the US Department of Transportation designated ten locations for testing autonomous vehicles.
- Rest of the World
- Japan has allowed autonomous vehicle testing since 2013, with a focus on Industry 4.0 and Society 5.0 initiatives.
- South Korea issued its first traffic permit for an autonomous vehicle to Hyundai Motors in 2016.
- China designated areas for testing autonomous vehicles with passengers in Beijing in 2019.
- South Australia became the first Australian state to adopt autonomous vehicle regulations to encourage manufacturers to test their vehicles.
Conclusion
- While autonomous vehicles are advancing rapidly, regulations are evolving more slowly.
- Regulations are often seen as transitional measures, requiring the presence of a human driver as technology undergoes testing.
- As technology becomes more reliable, regulations may evolve to no longer require human drivers.
- A significant challenge for the future is cybersecurity, as high-tech crimes pose risks to both conventional and autonomous vehicles.

Key Takeaways
- Autonomous vehicle regulations vary by country and state.
- Many countries are transitioning from requiring human drivers to potentially allowing fully autonomous vehicles.
- Cybersecurity is a growing concern as autonomous vehicles become more prevalent.