Lesson 5 – Achieved Environmental Benefits
Lesson Overview: In this lesson, we will explore the significant environmental benefits achieved through the implementation of Best Available Techniques (BAT) and other sustainable practices in various sectors. We will focus on key sectors, including energy, industry, agriculture, food & waste, nature-based solutions, transport, and buildings & cities, which have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future. Learners will understand the importance of transitioning to low-carbon alternatives and adopting climate-smart development practices to mitigate climate change and its impacts.
Lesson Objectives: By the end of this lesson, learners will be able to:
- Identify the main sectors and industries responsible for significant greenhouse gas emissions.
- Recognize the potential environmental benefits achievable through the adoption of BAT and sustainable practices.
- Understand the crucial role of global cooperation and individual action in achieving a low-carbon, climate-resilient future.
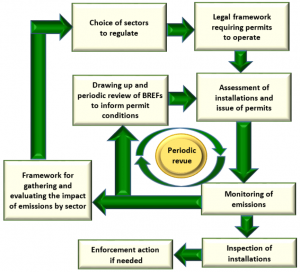
Simplified flowchart illustrating how BREFs fit in a regulatory regime
Lesson Content:
- Energy Sector and Emission Reduction
The energy sector is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to renewable energy sources and increasing energy efficiency, it has the potential to reduce emissions by a significant amount. This includes phasing out unabated coal and gas generation, adopting efficient and renewable heating and cooling systems, and ensuring reliable energy access for all. Electrification of industry and the use of green hydrogen are essential to decarbonize energy-intensive sectors.
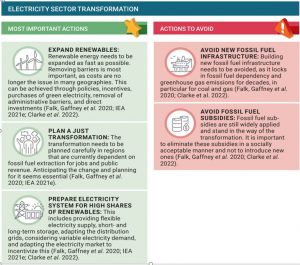
Actions that accelerate or hinder the transformation of the electricity sector
2. Industry Sector and Transformation
The industry sector accounts for a considerable share of global emissions. Achieving further emissions reductions requires electrifying industry, using new fuels, and promoting material and energy efficiency. Circular material flow and waste recycling are crucial to reducing emissions in this sector.

Actions that accelerate or hinder the transformation of the industry sector
3. Agriculture, Food & Waste Sector
Food systems are significant contributors to climate change and environmental degradation. Reducing food loss and waste, promoting sustainable diets, and improving food production methods can lead to substantial emissions reductions. Transforming food systems is essential for achieving climate goals and ensuring food security for all.
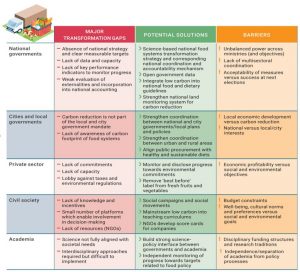
Potential solutions and barriers to food systems transformation by actor group
4. Nature-Based Solutions
Halting deforestation, ecosystem degradation, and restoring ecosystems can lead to substantial emissions reductions. Investing in land, freshwater, and marine ecosystems can increase climate resilience and improve air and water quality.
5. Transport Sector
The transport sector is responsible for a significant share of greenhouse gas emissions. Shifting to electric vehicles, promoting non-motorized transport, and improving public transportation can reduce emissions. Failure to decrease vehicle emissions could lead to a significant increase in deaths from exhaust fumes in cities.
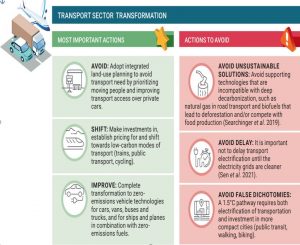
Potential solutions and barriers to food systems transformation by actor group
6. Buildings and Cities
Buildings account for a substantial portion of energy-related emissions. Reducing excess floor area, minimizing energy consumption, and adopting cleaner technologies for heating and cooling are essential steps to reduce emissions in the building sector. Circular economy principles can further contribute to emission reductions.
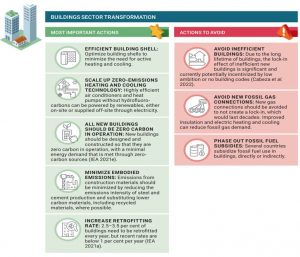
Actions that accelerate or hinder the transformation of the buildings sector
Conclusion:
Achieving environmental benefits and mitigating climate change requires concerted efforts across various sectors. By transitioning to sustainable practices, adopting BAT, and investing in renewable energy, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and build a more resilient future. It is essential for governments, industries, communities, and individuals to work together to embrace low-carbon alternatives, promote sustainable development, and address the challenges posed by climate change. Through collective action, we can make a positive impact and ensure a sustainable planet for future generations.