Lesson 2: DEFINITION OF BAT (Best Available Techniques)
In this lesson, we will explore the essential concept of Best Available Techniques (BAT) and its role in environmental regulation and industrial emissions control.
What is BAT?
- BAT stands for Best Available Techniques. It refers to advanced and proven techniques that aim to prevent and control industrial emissions and their broader environmental impact.
- These techniques are developed at a scale that allows for practical implementation under economically and technically viable conditions.
- Governments increasingly use BAT to establish emission limit values (ELVs) and other permit conditions for industrial installations, ensuring human health and environmental protection.
- BAT-based permit conditions can encompass ELVs, technical and management requirements, and monitoring requirements related to emissions, consumption, and waste generation.
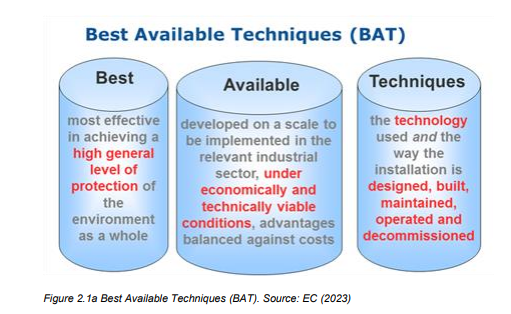
The Three Pillars of BAT
- BAT consists of three key pillars:
- Best: Denotes the most effective approach to achieve a high level of environmental protection.
- Available: Signifies that these techniques are developed at a scale suitable for implementation within the relevant industrial sector, considering economic feasibility.
- Techniques: Encompasses the technology used, as well as how an installation is designed, constructed, maintained, operated, and decommissioned.
The European Union’s Definition of BAT
- The European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive defines BAT as the most advanced stage in the development of activities and methods of operation.
- BAT serves as the foundation for emission limit values and other permit conditions, aiming to prevent or reduce emissions and their impact on the environment.
- “Techniques” include both technology and installation-related aspects.
- “Available techniques” are those developed at a scale allowing practical implementation, considering costs and advantages.
- “Best” signifies the most effective approach in achieving a high level of environmental protection.
BAT-AEPLs and Their Role
- BAT is used to derive BAT-associated environmental performance levels (BAT-AEPLs), including BAT-associated emission levels (BAT-AELs) and other environmental performance indicators.
- BAT-AELs represent emission levels achievable under normal operating conditions using BAT or a combination of BAT.
- BAT-AEPLs can also relate to material, water, and energy consumption, waste generation, pollutant abatement efficiency, and more.
- BAT-AEPLs contribute to sustainable chemistry, manufacturing efficiency, and other aspects of sustainable practices.
BAT Reference Documents (BREFs)
- BREFs play a crucial role in presenting BAT and BAT-AEPLs, along with relevant information.
- These documents are developed through stakeholder exchange and describe applied techniques, current emissions and consumption levels, and techniques considered for determining BAT.
- BREFs offer insights into BAT conclusions and emerging techniques.
BAT in Slovakia’s Legislation
- Slovakia introduced the term “Best Available Techniques” (BAT) into its legislation through Act No. 245/2003 Coll.
- The legislation aims to prevent and control environmental pollution.
- European Union directives have influenced Slovakia’s approach to BAT.
Benefits of BAT-Based Permitting
- Case studies highlight the advantages of BAT-based permitting, including:
- Significant reductions in industrial emissions, preventing air pollution and health damage.
- Enhanced competitiveness for companies.
- Sustainable practices leading to resource efficiency.
- Contributions to environmental and societal well-being.
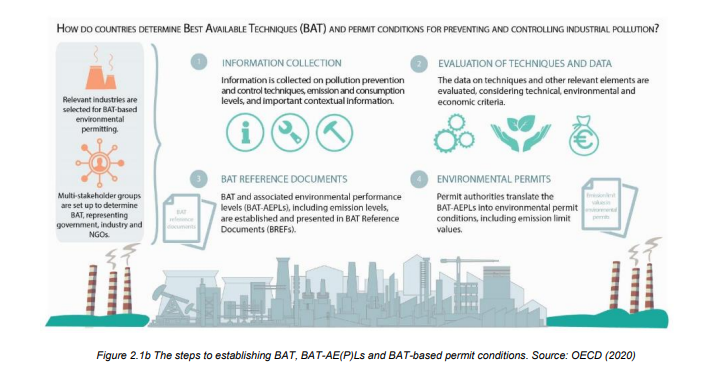
Establishing BAT and BAT-AEPLs
- The process of defining BAT and BAT-associated environmental performance levels (BAT-AEPLs) involves several steps.
- Each jurisdiction should define BAT within its environmental legislation, considering specific regulations and circumstances.
- BAT and BAT-AEPLs are key components of BAT-based permitting systems.
Conclusion
- BAT is a critical concept in environmental regulation, focusing on advanced techniques for industrial emissions control.
- It plays a vital role in promoting sustainability, protecting human health, and reducing environmental impacts.
- Understanding BAT and its implementation is essential for policymakers, regulatory officials, and individuals concerned with environmental issues.