Lesson 3: The concept of maintenance, the right to repair, and the impact of industry 4.0
In this lesson, we will explore the concept of maintenance, the emerging right to repair movement, and how Industry 4.0 is transforming maintenance practices in the modern world.
Expanding the Concept of Maintenance
- While maintenance is traditionally associated with production equipment and logistics tools, the rise of durable consumer goods and frequent replacements raises concerns about resource use and waste production.
- The broadening of the right to repair could bring significant changes to the maintenance and repair sector, promoting sustainability.
The Right to Repair
- The European Parliament has advocated for consumer rights to repair for over a decade and proposed concrete measures to make repairs more accessible and cost-effective.
- Legislative proposals include making repairs more appealing to consumers, requiring manufacturers to provide repair information, ensuring device durability and repairability, offering better consumer information, and extending warranties.
The Impact of Industry 4.0 on Maintenance
- Industry 4.0, the fourth industrial revolution, is reshaping maintenance activities by integrating cyber-physical tools, data processors, and information networks into production processes.
- This revolution builds on previous industrial advancements, incorporating digitalization technologies like cloud computing, Big Data, and artificial intelligence.
- Industry 4.0 enables the optimization of processes, efficient production, and competitiveness by breaking down physical barriers through data collection and knowledge sharing.
The Evolution of Maintenance
- Despite technological advancements in the industry, the fundamental definition of maintenance has remained consistent for over two hundred years.
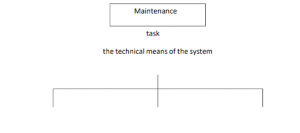
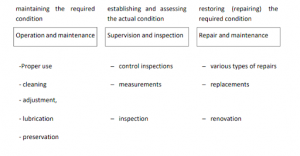
- Maintenance encompasses all activities needed to ensure the serviceability and proper use of fixed assets.
- It includes operations to maintain or restore required conditions, assess and qualify asset conditions, and prevent wear and tear from exceeding acceptable levels.
- Maintenance activities range from continuous tasks like cleaning, lubrication, and care to intermittent tasks such as repairs and replacements.
- Continuous maintenance minimizes disruptions to production, while repairs usually entail downtime.
- As industry and technology have evolved, maintenance has incorporated new tools and technologies, leading to the need for specialized maintenance technicians.
Preserving Functional Capacity
- The primary goal of maintenance is to preserve the functional capacity of equipment and installations while preventing failures.
- Maintenance practices aim to ensure the longevity, reliability, and efficiency of assets.
Conclusion
- Maintenance, the right to repair, and Industry 4.0 are interconnected concepts that play crucial roles in modern society.
- Expanding the right to repair can lead to more sustainable consumption practices.
- Industry 4.0 is transforming maintenance by integrating digital technologies, enhancing efficiency, and preserving assets’ functionality.
Read the textbook from page 26-35. You can find the textbooks’s content on this link.