Lesson 7 – Maintenance strategies
In this lesson, we will explore various maintenance strategies and systems, which are essential for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of machinery and equipment.
Understanding Maintenance Strategies
- Machine maintenance, also known as product aftercare or servicing, comes in various forms aimed at preserving the operational condition of products.
- Choosing the right maintenance strategy involves considering market demand, market penetration, operator needs, equipment requirements, design principles, spare parts availability, and environmental factors.
Implementing Maintenance Strategies
- Maintenance strategies can be categorized as long-term, strategic, or short-term, tactical.
- Long-term strategies include various maintenance regimes such as corrective, corrective replacement, planned preventive, preventive maintenance, and total maintenance.
- Short-term strategies encompass immediate solutions for unexpected issues.
Maintenance Systems
- Different maintenance systems have evolved to address the diverse nature of machinery failures and repairability.
- Various maintenance systems are selected based on economic considerations, including:
- On-demand maintenance and repair (“fire-fighting”).
- Planned preventive maintenance (PPM), either time-based or performance-based.
- Maintenance based on technical condition testing (diagnostics).
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM).
- Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM).
Maintenance and Repair on an As-Needed Basis or as Replacement for a Defect
- In this system, repairs occur only after a failure has happened.
- Failed components or main parts are repaired or replaced when needed.
- Regular care and lubrication are essential.
- Advantages include maximum utilization of parts, but disadvantages include unplanned downtime and the need for a significant spare parts inventory.
Planned Preventive Maintenance (PPM)
- PPM is a widely used maintenance system focused on preventing faults and unforeseen breakdowns.
- Regular inspections and repairs are carried out according to a predefined maintenance schedule.
- This system is prevalent in various industries, promoting operational reliability through planned inspections and repairs.
Preventive Maintenance Based on Technical Condition Testing (Diagnostics)
- PMM relies on component wear analysis and logic.
- However, it may not provide a precise answer due to factors like quality variations, operating conditions, and uncertainties.
- To maintain equipment in a fit state for use, periodic or continuous technical condition tests are employed during operation.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
- TPM, rooted in Japanese industry, engages all employees in preventive maintenance through small group activities.
- Operators take responsibility for routine machine maintenance.
- TPM includes steps such as improving equipment utilization, autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, training programs, and designing reliable machinery.
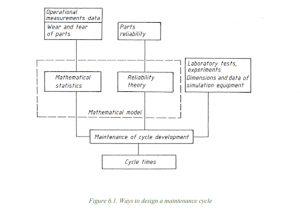
Establishing a Maintenance Cycle
- Machinery gradually loses usefulness during its service life until failure.
- Failures are influenced by operating conditions, time of use, and performance.
- To reduce breakdowns and downtime, a well-organized prevention strategy is necessary.
- A cycle schedule determines the intervals for inspections and repairs.
- Cycle schedules consider maintenance frequency, inspection and repair sequence, work types, and parameters (time, distance, etc.).
- Various methods, including wear analysis and economic calculations, are used to determine cycle times.
- Interventions are planned to prevent expected failures, based on operational, maintenance, and repair experience.
- Machine failure modes are often stochastic due to technical variations, material inconsistencies, manufacturing inaccuracies, and stress variations.
Conclusion
- Maintenance strategies are essential for preserving the operational condition of machinery and equipment.
- The choice of maintenance strategy depends on multiple factors, including market demand and equipment characteristics.
- Long-term and short-term maintenance systems cater to different needs.
- Preventive maintenance, based on both schedule and diagnostics, helps prevent unplanned breakdowns.
- Total Productive Maintenance involves all employees in machinery care.
- Establishing a maintenance cycle is crucial for maintaining equipment reliability and minimizing downtime.