Lesson 1: WELDING I – welded joint, requirements for welded joints, and weldability
In this introductory lesson, we will explore the fundamental concepts of welding, focusing on welded joints, the essential requirements for achieving quality joints, and the concept of weldability.
- WELDING
1.1. What is a Welded Joint?
- A welded joint is a permanent, non-detachable connection created by fusing two or more pieces of metal or alloys.
- Despite some limitations, welding is a highly versatile joining technology widely used in component manufacturing and large structure construction.
1.2. Requirements for Welded Joints
- The quality of welded joints is vital, not only for their local properties but also for their impact on the entire structure.
- Key local properties of a welded joint include:
- Lack of cracks
- Strength
- Toughness
- Inclusivity (freedom from voids or inclusions)
- Metallurgical structure
- These qualities are ensured through meticulous planning and adherence to work procedure specifications.
- The influence of welded joints on the construction involves:
- Safety against brittle fracture
- Fatigue resistance
- Corrosion resistance
- Achieving these requirements often depends on proper material selection and consideration of the stresses acting on the structure.
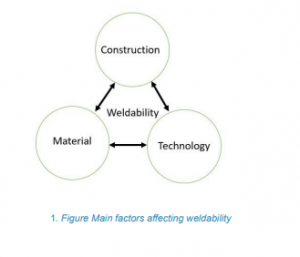
1.3. Understanding Weldability
- Weldability refers to the set of conditions under which a welded joint meets specific requirements.
- The definition of weldability is context-dependent, considering the joint’s requirements, material quality, and the welding technology used.
- There is no one-size-fits-all solution for weldability; conditions must be defined for each case.
- Weldability is categorized into two main types:
- Unconditional Weldability: When a welding technology consistently produces joints meeting requirements under normal conditions. Competence and workmanship remain essential.
- Conditional Weldability: For materials with poorer weldability properties, normal conditions may not suffice. Special conditions are required to ensure joint quality, such as preheating before welding, strict control of heat input, or immediate post-weld heat treatment.
Conclusion
- Welding is a versatile joining technology used in various industries.
- Understanding welded joints, the requirements they must meet, and the concept of weldability is fundamental to producing reliable and safe welded structures.
- Successful welding requires careful planning, skill, and adherence to specific conditions for each joint.
In this lesson, you’ve been introduced to the core concepts of welding, including welded joints, their requirements, and the concept of weldability. These fundamentals are crucial as we delve deeper into the world of welding techniques and applications in upcoming lessons.