Lesson 2: Concepts and the importance of the GVC
In this lesson, we will explore the concept of Global Value Chains (GVCs) and their significance in today’s global economy.
- Introduction to Global Value Chains (GVCs)
- The concept of Global Value Chains was introduced by Michael Porter in his 1985 book “Competitive Advantage.”
- GVCs are sets of activities that a firm performs to deliver valuable products or services to the market.
- A GVC consists of five primary activities:
- Inbound logistics: Receiving raw materials, warehousing, and inventory management.
- Operations: Converting raw materials into finished products or services.
- Outbound logistics: Delivering the final product or service to the end user.
- Marketing and sales: Strategies to incentivize customers to purchase, including advertising and pricing.
- Post-sale services: Activities aimed at enhancing consumer experiences, such as customer services and maintenance.
- Secondary or Support Activities in GVCs
- GVCs can include secondary or support activities that enhance the efficiency of primary activities.
- These support activities encompass procurement, technology research, product development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure building.
- Each activity contributes to creating and adding value at different stages of the value chain.
- Evolution from Supply Chains to GVCs
- Initially, discussions on supply chains were logistics-focused.
- Since the mid-1990s, global manufacturing networks have become increasingly integrated and interdependent.
- Supply chains now encompass broader business functions and processes both within and across companies.
- Defining Global Value Chains
- The Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP) defines a supply chain as the links between companies that exchange materials and information.
- It spans from acquiring raw materials to delivering finished goods to end users.
- Key functions include material supply, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Globalization of Value Chains
- Global Value Chains (GVCs) or Global Supply Chains (GSCs) extend the concept internationally.
- GVCs respond to the global production fragmentation, where various entities in different countries perform functions along a value chain.
- GVC-related international transactions are crucial in cross-border trade and drive structural changes in the world economy.
- Factors Contributing to GVC Expansion
- Decreasing trade costs, including tariff reductions and improved logistics, have fueled GVC expansion.
- Regulatory reforms in transport and infrastructure sectors have enhanced logistical efficiencies.
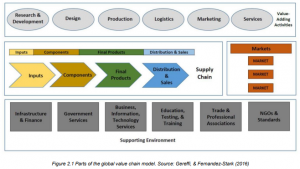
- Components of the Global Value Chain Model
- The GVC model consists of four key components: value-adding activities, supply chain, end markets, and the supporting environment.
- Value-adding activities involve research, design, manufacturing, logistics, marketing, sales, and services.
- The supply chain includes stages like materials/inputs, components/intermediates, final products, and distribution/sales.
- End markets represent product-specific characteristics and buyer demographics.
- The supporting environment encompasses factors that facilitate value creation, such as regulations, standards, and infrastructure.
- Importance of Global Value Chain model
- GVCs play a vital role in today’s global economy, contributing to a significant share of international trade, global GDP, and employment.
- They link firms, workers, and consumers worldwide, often providing opportunities for developing countries to integrate into the global economy.
- The GVC framework offers a holistic view of global industries and helps policymakers address development challenges.
- It allows the examination of various aspects, from emerging economies’ roles to environmental concerns and private regulations.
Conclusion
- Understanding the concept and importance of Global Value Chains is crucial in navigating today’s interconnected global economy.
- GVCs shape industries, trade, production, and employment, making them a central focus for policymakers, researchers, and businesses.
- They offer opportunities for countries to participate in the global economy effectively and promote economic development and job creation.