Lesson 8: Management of maintenance
In this lesson, we will delve into the essential aspects of managing maintenance systems to ensure the efficient operation of machinery and equipment.
Understanding Maintenance Management
- Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in the organization and management of maintenance.
- Maintenance strategies and management systems vary depending on factors, with technical and technological production levels being among the most crucial.
The Basic Concept of a Maintenance Management System
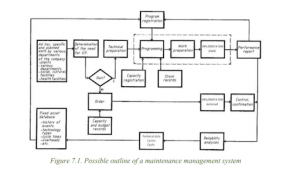
- A maintenance management system comprises three fundamental modules, each serving specific functions:
- Technical and Cost Information System for Maintenance: Provides rapid and realistic feedback on operational data.
- Spare Parts Management: Answers questions regarding spare parts ownership, availability, and allocation.
- Planning and Programming: Manages human and material resources for equipment and schedules maintenance procedures.
Implementation of the Management System
- Maintenance management involves three main activities:
- Issuing instructions.
- Providing instructions, receiving information, and giving feedback.
- Corrective intervention based on a comparison of information with instructions.
- Maintenance needs can be categorized as planned (predefined) or ad hoc tasks.
- Work orders are generated based on these needs and assessed to determine whether in-house or outsourced work is preferable.
- Technical preparation is essential for in-house work, ensuring prerequisites are met.
- A monthly program is established for preparatory work.
- Work vouchers are provided for clear task descriptions, parts usage, and execution time.
- Direct feedback after tasks ensures control and updates records for ongoing analysis.
- Repairs using external capacities are also managed for uniformity.
- Reliability studies help plan maintenance and assess equipment for refurbishment or decommissioning.
- Operational documentation is a critical aspect of the management system.
Integrated Management Systems, CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems)
- Integrated maintenance management systems optimize the use of resources for keeping production equipment in working order.
- These systems encompass scheduling routine maintenance tasks, monitoring equipment conditions, anticipating breakdowns, determining optimal maintenance times, and ensuring thorough preparations.
- Computerized maintenance and repair systems are essential for solving various management problems, such as spare parts management, equipment condition monitoring, and efficient maintenance planning.
- These systems should be designed to avoid “data silos” and should be tailored to meet specific needs.
Conclusion
- Effective maintenance management is crucial for the efficient operation of machinery and equipment.
- Maintenance strategies and systems depend on factors like technical and technological levels of production.
- A maintenance management system comprises three key modules: technical and cost information, spare parts management, and planning and programming.
- Implementation involves issuing instructions, providing feedback, and corrective interventions.
- Computerized maintenance management systems are vital for solving maintenance-related challenges and ensuring efficient resource utilization.