Lesson 1: The Historical Overview, THE CLUB OF ROME, and THE FIRST CRISES ON A GLOBAL SCALE
In this lesson, we’ll take a historical journey to understand how human activities have shaped the environment and society’s response to global challenges.
Historical Overview
- The process of environmental change began with the increasing human population and expanded territories.
- Early humans relied on large prey animals for sustenance, which, if overhunted without consideration for their reproduction, led to population declines and species extinction.
- Transition from foraging to agriculture and deforestation marked a shift from a nomadic lifestyle to settled communities during the Middle Ages.
- The Industrial Revolution significantly transformed the environment by industrializing production and rapidly expanding urban areas.
- World War II and post-war economic and commercial changes further influenced the environment and global economies.
The Role of the Club of Rome
- Founded in 1968, the Club of Rome aimed to explore the limits of Earth’s systems and their interactions.
- Key questions included the sustainability of exponential population and capital growth, the existence of hunger zones, and meeting the world’s basic needs.
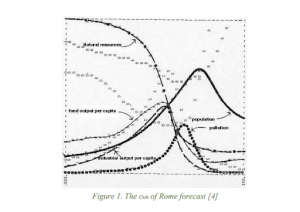
- Their 1972 report, “The Limits to Growth,” introduced a computer-based world model highlighting the depletion of non-renewable resources and its consequences.
- Reactions to the report varied, with some embracing its findings and others resisting change due to vested interests.
The First Global Crises
- The oil crises of 1973 and 1979, triggered by OAPEC’s use of oil as a political weapon, were the first recognized global crises.
- These events impacted Western economies and contributed to the disintegration of the Soviet Union and Eastern Socialist bloc.
- The report did not yet include climate change projections, but global warming’s early effects were evident in droughts, poor harvests, and floods worldwide.
- The interconnected nature of these events foreshadowed future challenges, including climate-induced migration.
Conclusion
- A historical overview reveals the evolving relationship between human activities, environmental changes, and global responses.
- The Club of Rome’s pioneering report raised awareness of sustainability issues, but societal resistance to change persisted.
- The first global crises, such as the oil shocks, hinted at the complexity and interconnectedness of global challenges.
- Understanding these historical contexts is crucial for addressing contemporary environmental and societal issues.
Read the textbook from page 1-7. You can find the textbooks’s content on this link.